Stay Ahead with Expert-Led Insights
Navigating Complexity. Driving Progress. Creating Lasting Impact.
Welcome to the TeKnowledge Insights hub! Here, you’ll find a blend of strategic perspectives, real-world case studies, and expert analysis designed to empower organizations to navigate challenges and seize new opportunities.
Explore the insights that matter most. Stay informed, gain new perspectives, and discover how businesses worldwide are unlocking new opportunities with TeKnowledge.
Stay Ahead with Expert-Led Insights
Navigating Complexity. Driving Progress. Creating Lasting Impact.
Welcome to the TeKnowledge Insights hub! Here, you’ll find a blend of strategic perspectives, real-world case studies, and expert analysis designed to empower organizations to navigate challenges and seize new opportunities.
Explore the insights that matter most. Stay informed, gain new perspectives, and discover how businesses worldwide are unlocking new opportunities with TeKnowledge.
All Categories
The latest developments, strategic partnerships and milestones.
- News & Company Updates
- 72% of the participants are women from rural areas across the country.
- The program is funded by the Ministry of Labor as part of their national employability strategy, Brete.
- This initiative is supported by various organizations committed to technological development and workforce integration beyond the Greater Metropolitan Area of San José.
San José, September 2024. – A total of 260 individuals, predominantly women from rural regions of Costa Rica, will embark on an intensive cloud computing training program in the second week of September. This initiative is designed to equip participants with the essential skills needed to thrive in the fast-evolving field of cloud technology, with a focus on enhancing their employability.
The “Cloud Support Specialist” program is financed by the Ministry of Labor and Social Security of Costa Rica through the Empléate program and the National Strategy for Employability and Human Talent, Brete.
“Through Brete, our goal is to improve the employability of 220,000 people, particularly young individuals, women, and those residing outside the Greater Metropolitan Area. This advanced training initiative exemplifies our commitment to investing in the country’s human capital, providing them access to quality jobs and contributing to the digital economy,” said Andrés Romero, Minister of Labor and Social Security of Costa Rica.
TeKnowledge, the implementing organization, will deliver the training, ensuring that participants acquire the necessary skills for integration into the technological job market.
“Our extensive experience in training tech talent has given us deep insights into the sector’s needs, especially in cloud computing. At TeKnowledge, we strive to offer programs that not only impart technical knowledge but also prepare participants to tackle real-world challenges in the job market. We are proud to contribute to the professional growth of these individuals, helping them become experts in one of the most dynamic and in-demand areas of technology today,” said Jeannie Bonilla, Country Manager of TeKnowledge.
The project is supported by Microsoft and is designed to provide comprehensive training in Microsoft Azure, operating systems (Linux/Windows), PowerShell, Active Directory, databases, networking, security, cloud architecture, and preparation for the AZ-900 certification. This intensive four-month course, delivered virtually, will emphasize hands-on practice and the application of knowledge.
“We are proud to support initiatives that make a tangible difference in people’s lives, promoting talent development and technological inclusion. This program not only empowers women and rural communities but also contributes to strengthening employability, developing digital skills, and narrowing the talent gap in Costa Rica’s tech sector,” added Ineke Geesink, Country Manager at Microsoft Costa Rica.
In addition to technical training, participants will receive instruction in professional skills and job interview preparation, facilitating a smooth transition into cloud computing roles.
Upon completion of the program, participants will receive job placement assistance in the sector, with opportunities to take on roles such as specialized technical support in the cloud, systems administrators, and cloud solutions consultants. Moreover, they will be prepared to take the AZ-900 certification exam, earning a globally recognized credential that will further enhance their professional standing in the job market.
Source (Spanish): Costa Rica: 260 jóvenes inician programa de formación en la nube con foco en la empleabilidad – Revista Summa
- Case Studies & Use Cases
Navigating the Cyber Battlefield: The Role of AI in Modern Cybersecurity
Organizations today navigate a treacherous digital landscape, where valuable data and critical operations are constantly under siege by ever-evolving cyber threats. The pressure to fortify defenses is immense, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerges as a potential game-changer, offering unparalleled capabilities for proactive defense. However, in the wrong hands, AI can turn into a formidable adversary. The cyber battlefield is becoming increasingly complex, demanding a nuanced understanding of AI’s dual potential as both a shield and a weapon.
This blog provides a critical exploration of AI in cybersecurity. It dissects the immense defensive capabilities of AI, unveils its potential threats, and charts a course towards leveraging its power responsibly.
AI: Revolutionizing Industries with Its Superpowers
AI’s enormous potential lies in its ability to surpass human capabilities in several key areas. AI’s speed and scalability are unmatched; algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in milliseconds, identifying patterns and anomalies that would take humans years to detect.
Beyond speed, AI excels at Natural Language Processing (NLP), understanding and extracting meaning from human language with remarkable accuracy. Additionally, AI boasts the unique ability for continuous learning. Like a tireless student, it evolves with every interaction, refining its detection models and adapting to new circumstances and conditions.
AI also breaks down language barriers, operating multi-lingually. It can analyze data and threats in various languages, providing comprehensive capabilities regardless of the attacker’s or defender’s origin. Ultimately, AI’s unique capabilities make it a formidable ally in the fight against cybercrime, offering a level of defense that human analysts alone cannot achieve.
AI in Cyber Defense: Challenges to Consider
While AI presents exciting possibilities for bolstering cyber defenses, it’s crucial to acknowledge the challenges it introduces. Like any powerful tool, its effectiveness hinges on responsible use and understanding its limitations.

False Positives: AI engines are not immune to generating false positives. Imagine a scenario where a security team is bombarded with constant alarms triggered by AI, only to discover most are false positives. This “alert fatigue” can overwhelm security personnel, diverting valuable resources from investigating genuine threats. Balancing sensitivity with accuracy is crucial to ensure AI serves as a valuable ally, not a nuisance.
Transparency: AI models excel at pattern recognition and anomaly detection, but their decision-making process is often opaque. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to understand why a specific threat was flagged, hindering efforts to refine the model and ensure its correctness.
Bias: AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the training data harbors biases, the model can inherit and perpetuate them, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Careful data selection and bias mitigation techniques are essential to ensure AI serves justice, not prejudice.
Cost-Effectiveness: Implementing and maintaining complex AI systems requires significant investment, both in terms of financial resources and technical expertise. Smaller organizations may find this barrier to entry insurmountable, potentially widening the security gap between different entities. A managed Security Operations Center (SOC) can serve as a great solution in these cases, allowing smaller organizations to still enjoy all that AI-assisted cyber defense has to offer.
Human Oversight: While AI excels at automation and pattern recognition, human judgment and critical thinking remain indispensable. Overreliance on AI solutions without proper human oversight can be misleading, causing us to neglect crucial details or overlook emerging threats that require nuanced interpretation.
By acknowledging these challenges and proactively addressing them, we can harness the true potential of AI in cyber defense while mitigating its risks.
AI’s Defensive Toolbox: Bolstering Defenses Across the Cybersecurity Spectrum
For defenders in the ever-escalating cyber war, AI has emerged as a powerful ally, wielding a unique set of skills that bolster defenses and turn the tide against attackers. The most popular AI-enhanced cybersecurity practices include:
- Enhanced Threat Detection and Analysis:
An AI-powered IDS/IPS system acts like a tireless security analyst meticulously scrutinizing every corner of the organization’s digital landscape. AI algorithms sift through massive amounts of data such as system logs and network traffic, uncovering hidden patterns and anomalies that might indicate impending attacks or potential intrusions. They excel at recognizing subtle deviations from normal behavior, even those cleverly disguised by attackers, allowing defenders to proactively address threats before they materialize. These systems also adapt to evolving attack patterns and learn from past incidents, offering proactive threat detection and prevention capabilities.
- Phishing and Social Engineering Detection:
Social engineering and phishing attacks often rely on manipulating human emotions and exploiting trust. AI’s language processing prowess can be leveraged to analyze emails and messages, recognizing suspicious wording, sender behavior, and even subtle visual cues that betray fraudulent attempts.
- Automated Response Systems:
In the event of a security breach, every second counts. AI-powered systems can automatically trigger countermeasures like blocking suspicious IP addresses or quarantining infected files upon threat detection, minimizing potential damage. This swift intervention can significantly limit the impact of an attack.
- Threat Intelligence:
AI automates data analysis from various sources, including dark web and threat feeds. Advanced analytics analyze past attacks and attacker behavior to predict future trends, uncover hidden connections, prioritize high-risk threats, and predict future attack vectors, empowering proactive defense strategies.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
Attackers constantly devise new tactics and exploit novel vulnerabilities. Unlike traditional security solutions, AI models possess the remarkable ability to continuously learn and adapt. As they encounter new threats, they refine their detection capabilities, ensuring defenses remain agile and effective against even the most sophisticated adversaries.
- Vulnerability Identification and Prioritization:
AI-based tools excel at performing critical tasks like scanning organizational systems to identify and rank vulnerabilities based on their potential impact and exploitability. This allows for effective resource allocation, keeping the focus on patching the most critical vulnerabilities first and minimizing attack surfaces.
- Anti-Malware and Antivirus Software:
Traditional signature-based detection struggles with ever-evolving malware. AI-powered solutions leverage behavioral analysis and machine learning to identify and neutralize even zero-day threats, providing real-time protection against constantly morphing malicious software.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) & Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR):
AI fuels these integrated platforms by ingesting and analyzing data from diverse sources, correlating events, and identifying complex security incidents. SOAR leverages AI for automated responses, streamlining incident resolution and minimizing damage.
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA):
UEBA leverages AI to analyze user behavior patterns and entity activity across systems, detecting unusual login attempts, file access anomalies, and communication with suspicious entities, helping identify potential insider threats and data breaches early on.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention:
AI models trained on historical fraud patterns can analyze transactions and user behavior in real time, identifying suspicious activities like unauthorized access attempts, money laundering attempts, or fraudulent account creation. This proactive approach mitigates financial losses and protects sensitive data.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
AI-powered DLP solutions go beyond traditional keyword matching. They analyze data content, context, and user intent to identify sensitive information at risk of unauthorized exfiltration, preventing accidental or malicious data leaks and safeguarding intellectual property and customer privacy.
It’s important to remember that AI is a powerful tool, but not a magic bullet. Its effectiveness relies on high-quality data, clear objectives, and continuous improvement. By responsibly integrating AI into these diverse defensive areas, organizations can build a more robust and adaptable cybersecurity posture.
The Dark Side of the Moon: How Attackers Wield AI in Cyber Warfare
While AI presents a powerful tool in the hands of cybersecurity defenders, it’s crucial to acknowledge its potential misuse by malicious actors. In the wrong hands, this technology can become a sophisticated weapon, capable of supporting devastating attacks that exploit human vulnerabilities and bypass traditional defenses. Let’s delve into some of the ways AI can be weaponized:

- The Art of Deception: Personalized Phishing
Imagine an employee receiving an email that appears to be from a trusted colleague, perfectly mimicking their writing style and referencing specific details about joint work. This becomes possible with AI-powered phishing attacks. These malicious programs can analyze vast amounts of personal data, crafting highly targeted emails that bypass traditional spam filters and exploit victims’ trust.
- The Shape-Shifting Threat: Autonomous Malware on the Loose
Traditional malware often generates static signatures that allow security software to detect and neutralize it. But what if malware could learn and adapt? AI-powered malware can do just that, analyzing its environment and modifying its behavior to evade detection. For example, attackers can develop malware that actively hides its presence within infected systems. These sophisticated programs can manipulate system logs, disrupt security software, and even camouflage themselves as legitimate processes. This “living” threat poses a significant challenge, demanding innovative defense strategies.
- Lies That Seem Real: Deepfakes and Disinformation Campaigns
The ability to create realistic fake videos and news articles using AI, known as deepfakes, raises serious concerns. Malicious actors can leverage this technology to wreak havoc, manipulate public opinion, and even damage reputations. A deepfake video of a CEO making false statements could cause chaos in financial markets. Another example is a voice deepfake used to bypass a multi-factor authentication solution for a bank.
- Social Engineering 2.0: Automating Manipulation
Social engineering, the art of exploiting human trust and emotions, is a common tactic used by cyber attackers. AI can take this to a new level by automating tasks like crafting personalized messages, identifying vulnerable individuals, and mimicking human conversation patterns. This harsh prospect highlights the need for increased awareness and critical thinking skills to counter such attacks.
- Breaking Down the Wall: Password Cracking
Brute-force password attacks involve trying countless combinations until the correct one is found. AI can significantly accelerate this process by implementing predictive analytics and improving brute-force techniques. This underscores the importance of strong, unique passwords and multi-factor authentication to thwart such attempts.
- Poisoning the Well: Data Poisoning Attacks
Imagine feeding false or manipulated data into machine learning models used by organizations for various purposes. This practice, known as data poisoning, can have severe consequences if left unchecked. Attackers can use AI to generate and inject such poisoned data, compromising the integrity of models and potentially leading to disastrous outcomes.
- Scouting the Territory: AI-Powered Reconnaissance
Before launching a major attack, attackers often engage in reconnaissance, gathering information about their target’s systems and vulnerabilities. AI can automate this process, analyzing vast amounts of publicly available data and actively probing networks for weaknesses. This highlights the importance of maintaining strong network security and being mindful of what information is shared publicly.
The integration of AI into attacker arsenals poses a chilling prospect. Not only could it enable the development of more complex, sophisticated, and targeted attacks, bypassing even robust defenses, but it could also democratize cybercrime and lower the barrier to entry. This means that even less skilled individuals may use AI-powered tools to launch sophisticated attacks with relative ease. This democratization of cybercrime opens Pandora’s box of potential threats, exponentially increasing the attack surface defenders must contend with.
To better understand this battle of forces, consider a practical example – a ransomware attack.
The AI Ransomware Showdown: Attack vs Defense

Scenario: In our example, a leading financial services company, publicly traded and heavily interconnected with many other entities, is targeted by a sophisticated cybercriminal group planning a multi-pronged ransomware attack using AI.
Attacker’s AI Arsenal
- Personalized Phishing: The group employs AI to analyze social media profiles and internal emails of the company’s key personnel. Tailored phishing emails, mimicking communication style and referencing specific projects, are sent to individuals with access to critical systems.
- AI-Powered Malware: Phishing emails contain malicious attachments. Upon opening, the AI-powered malware adapts to the victim’s system, exploiting specific vulnerabilities and evading traditional signature-based detection.
- Social Media Manipulation: In parallel, bots powered by AI flood social media with negative comments and misinformation, further pressuring the company to comply with the attacker’s demands.
- Lateral Movement and Data Exfiltration: The malware grants remote access, allowing the criminals to move laterally across the network, identifying and exfiltrating valuable data using AI-powered data extraction tools.
Defender’s AI Shield
- Anomaly Detection: AI-powered systems analyze network traffic and user behavior, detecting deviations from normal patterns triggered by phishing emails and malware activity.
- AI-Driven Threat Hunting: Upon anomaly detection, AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data logs, identifying the root cause of the attack and the specific malware used.
- Automated Containment: The AI system automatically isolates compromised systems and restricts lateral movement, preventing further data exfiltration.
- Deepfake Detection: Advanced AI models trained on deepfake characteristics analyze the CEO video, identifying inconsistencies and flagging it as a fabrication.
- Social Media Monitoring: AI-powered sentiment analysis tools track social media trends, identifying and countering misinformation campaigns orchestrated by the attackers’ bots.
- Data Backups and Restoration: Regularly backed-up data, protected by immutable storage solutions, are readily available for restoration, minimizing the impact of data exfiltration.
The Outcome
The company’s AI-powered defenses successfully detect and contain the attack, minimizing data loss and operational disruption. The deepfake is exposed, and social media manipulation attempts are countered. While the cybercriminals might adapt their tactics, the company’s continuous improvement of its AI defenses ensures a resilient posture against future AI-powered threats.
Next, let’s explore how AI empowers two specific areas that are critical in today’s organizational cyber defense: Bridging the cybersecurity skills gap and enhancing managed SOCs.
The Role of AI in Bridging the Cybersecurity Skills Gap
The cybersecurity industry faces a persistent and significant skills gap, leaving organizations vulnerable to attacks. AI presents several promising opportunities to address this talent shortage and empower security teams:
Automating Repetitive Tasks: SOC analysts often spend valuable time on mundane tasks like log analysis and threat detection. AI-powered tools can automate these repetitive processes, freeing up analysts to focus on higher-level strategic thinking, incident investigation, and threat hunting. This not only enhances their efficiency but also increases job satisfaction and reduces burnout.
Democratizing Security Expertise: AI-powered security solutions can offer guided assistance to analysts, even those with limited experience. By suggesting relevant playbooks, providing context-specific knowledge bases, and highlighting potential leads, AI can bridge the knowledge gap and empower analysts to make informed decisions without extensive cyber expertise.
Upskilling the Workforce: Continuous learning is crucial in cybersecurity. AI-powered training platforms can personalize learning experiences for analysts, identifying their knowledge gaps and recommending relevant courses, tutorials, and simulations. This adaptive approach ensures they stay up-to-date with the latest threats and techniques, closing the skills gap over time.
Identifying and Recruiting Talent: AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify individuals with skills and aptitudes suitable for cybersecurity roles. This can help organizations recruit more effectively, tapping into hidden pools of talent that might not have traditionally considered a career in cybersecurity.
Some concerns exist about AI perpetuating biases in recruitment and decision-making or creating overreliance on automated systems. However, AI can play a significant role in addressing the cybersecurity skills gap if integrated carefully, with consideration of ethical implications and a focus on human-AI collaboration to ensure a secure and empowered future for the cybersecurity workforce.
AI Powers Up the Managed SOC: Security Operations Overhauled
Security Operation Centers (SOCs) play a critical role in safeguarding organizations against an ever-evolving cyber threat landscape. As attackers increasingly leverage AI in their arsenal, it’s crucial for SOCs to adopt this game-changing technology to stay ahead of the curve. Managed SOCs, offering expertise and resources to various organizations, can leverage AI to significantly enhance their capabilities in several key areas.

By integrating AI into their operations, managed SOCs can unlock a new level of efficiency, speed, and accuracy in detecting, investigating, and responding to cyber threats. This not only benefits individual organizations but also strengthens the overall cybersecurity posture of the broader ecosystem. AI-powered managed SOCs also offer smaller organizations the opportunity to leverage advanced AI defenses at a reasonable cost, helping to mitigate the security gap between different entities.
Summary
As the arms race between attackers and defenders intensifies, both sides leverage AI to outmaneuver each other. This escalating battle underscores the urgent need to establish clear protocols for human oversight and accountability.
It’s important to remember that AI is a tool, not a silver bullet. Its effectiveness hinges on robust data quality, clear goals, and continuous improvement strategies.
The path forward lies in responsible development, ethical implementation, and a clear understanding of both the immense power and inherent limitations of this transformative technology. This approach is crucial for building trust and ensuring public acceptance of AI-powered solutions.
TeKnowledge stands at the forefront of leveraging AI to enhance cybersecurity. As cyber threats continue to evolve, our expertise and innovative approaches ensure that our customers are equipped to face even the most sophisticated cyber threats. By understanding both the defensive and offensive potential of AI, TeKnowledge helps organizations navigate the complexities of modern cybersecurity, safeguarding their operations and data in an increasingly perilous digital world.
- Blog & Industry Trends
The business landscape is evolving, making digital transformation crucial for organizations to remain competitive and attract new customers. This journey not only aligns with organizational goals but also fosters customer satisfaction. In today’s environment, digital transformation is more than a buzzword; it is a strategic imperative for thriving in the modern marketplace.
It encompasses various technologies and strategies that can help businesses streamline their operations and enhance customer experience. But what exactly is digital transformation? How does it impact the customer experience? And how can companies get started with it?
This article explores the different aspects of digital transformation and how they can be used to reimagine the customer journey in the digital age. From personalization to automation, we will cover the latest trends and techniques driving the customer experience forward.
The Role and Impact of Digital Transformation in Today’s World
Digital transformation is reshaping industries across sectors, revolutionizing business models and operations. Studies show that organizations embracing this change will contribute about $54 trillion to the US GDP. As customer expectations evolve, digital transformation becomes a top priority to deliver a personalized customer experience. With the integration of digital technologies, organizations can provide a better customer experience, leveraging real-time data and insights.
The New Age Customer in the Digital Era
Digital technologies have empowered customers, providing them with more information and choices. As a result, customers now expect seamless multi-channel experiences across various touchpoints. Personalization and relevant content are crucial in meeting these customer expectations. Social media and online reviews play a significant role in shaping customer purchasing decisions. The digital era has transformed the customer journey, moving from awareness to advocacy.
Organizations must prioritize integrating digital experience in their business landscape to ensure better customer experience. Digital transformation is not just about technology; it requires a human touch to truly understand and cater to the needs of the new kind of modern buyer. Happy customers are the top priority, and businesses must adapt accordingly to stay competitive.
How Digital Transformation is Influencing Customer Behavior
Digital transformation has significantly influenced customer behavior. With the rise of digital technologies, customer expectations have evolved, emphasizing convenience and speed more. Here are a few ways of how customer behavior has changed:
1. Multi-channel expectations: In the past, customers might have been happy to interact with brands only through a single channel, like calling or going to a physical location. But in today’s digitally altered environment, customers demand seamless interactions across all channels. For instance, they might begin looking at products on a mobile app, continue a desktop website, and finish purchasing using a chatbot or a smart speaker.
2. Digital engagement: Consumers are increasingly likely to communicate with brands online. Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram are just a few examples of the social media sites that are now essential communication tools. Customers actively engage with brands by offering feedback, posting queries, and making suggestions in addition to simply following them.
3. E-commerce dominance: The convenience of online buying and the growth of e-commerce platforms have significantly altered consumer purchase patterns. Nowadays, consumers frequently forego traditional brick-and-mortar retailers in favor of online product browsing and purchases. The COVID-19 era accelerated this pattern as more people turned to internet buying to meet their demands.
4. Mobile transformation: Customer behavior has been revolutionized by mobile gadgets. Due to the widespread use of smartphones and tablets, consumers may now access information, purchase, and connect with brands anytime and anywhere. Mobile apps and flexible websites have become crucial for businesses to serve this mobile-savvy customer base.
5. Real-time support: Organizations can now offer real-time customer care thanks to solutions like chatbots powered by artificial intelligence and digital transformation. Customers no longer desire to be placed on hold or wait for a response to emails. They need prompt and effective assistance around the clock, and organizations that use chatbots and automated support systems may successfully meet this demand.
Why do Businesses Need Digital Transformation?
Businesses need a digital transformation to stay competitive in today’s digital landscape. Meeting customer expectations for a seamless omnichannel experience and personalized interactions requires leveraging new technologies and business models. Digital transformation is a long-term strategy for businesses to thrive in the digital age.
Starting with Digital Transformation – The First Steps
Define goals: Defining the organization’s goals and vision for digital transformation is the first crucial step for business leaders. It sets the direction and purpose for the entire digital transformation journey.
Evaluate current technology stack: Assessing the current state of digital technologies and infrastructure is essential. This evaluation helps identify gaps or areas needing improvement to support the transformation process effectively.
Create a transformation strategy: Once these assessments are complete, creating a digital transformation strategy becomes imperative. This strategy outlines the roadmap and action plan for implementing change and achieving the desired outcomes.
Find a digital transformation solution: Partnering with the right technology vendors can provide expertise and solutions to drive successful digital transformation. An effective digital transformation partner can provide training to your employees. This will foster a culture of innovation within your organization.
Strategies for Implementing Digital Transformation
Implementing digital transformation requires a strategic approach to ensure success. These are the steps to build a digital transformation strategy:
Prioritize customer needs: Prioritizing initiatives based on customer needs and business impact is crucial. By understanding what your customers want and aligning it with your organization’s goals, you can focus on delivering a better customer experience.
Develop a roadmap: Developing a roadmap with clear milestones and timelines provides a structured framework for your digital transformation journey. Embracing agile methodologies allows you to adapt quickly to evolving customer demands.
Upskill your workforce: While digital transformation is beneficial to your business, you need to consider training your workforce on the tools and techniques to embrace the workforce. This will enable everyone on the team to be on the same wavelength when it comes to digital transformation.
Encourage collaboration: Foster strong communication and collaboration across departments to break down silos and enable a seamless flow of information.
Measure: Continuously measuring and analyzing the impact of your digital transformation efforts ensures that you stay on track and achieve your organization’s goals.
Reimagining the Customer Journey in the Digital Age
The customer journey has evolved to encompass multiple online and offline channels in the digital age. Organizations must map out this journey to provide a seamless customer experience, identifying pain points and opportunities along the way. Integrating digital touchpoints is crucial in ensuring a positive customer experience. Automation and personalization significantly enhance the customer journey, allowing businesses to cater to individual needs and preferences.
Organizations can optimize the customer journey by leveraging data and analytics, tailoring their offerings and interactions accordingly. Reimagining the customer journey in the digital age should be a top priority for organizations seeking to cultivate happy and loyal customers.
Tools and Techniques to Enhance Digital Customer Experience
To enhance the digital customer experience, organizations can leverage various tools and techniques. Integrating these tools and techniques into the digital transformation journey aligns with an organization’s goals and ultimately leads to happy customers.
Customer relationship management (CRM): Customer relationship management (CRM) systems are crucial in managing customer data effectively.
Digital marketing: Digital technologies like apps and social media provide platforms for engaging customers and creating personalized experiences. Targeted marketing campaigns can be designed to cater to specific customer segments, driving better engagement and satisfaction.
Automation and chatbots: Automation and chatbots enable real-time support, ensuring quick resolutions to customer queries.
Analytical tools: By using analytics, organizations can gain valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing for continuous improvement of the digital customer experience.
The Importance of a Seamless Multi-Channel Experience
Customers today expect a consistent and seamless experience across all channels. More is needed for organizations to operate their online and offline channels independently. Instead, they must integrate these channels to create a holistic, unified customer experience. Accessibility and user-friendly interfaces are crucial in delivering a seamless multi-channel experience. Leveraging mobile devices and in-store technologies can enhance the customer experience, offering convenience and personalized interactions.
Moreover, organizations must continuously adapt to changing customer preferences and behaviors to ensure a seamless multi-channel experience that meets the evolving needs of the modern buyer. Ultimately, prioritizing a seamless multi-channel experience leads to happy customers and better business outcomes.
How Does Multi-Channel Experience Benefit Customers?
Multi-channel experiences benefit customers by providing a seamless and convenient way to interact with a brand. Customers can effortlessly switch between channels, choosing the most convenient one for their needs. Consistent messaging and branding across channels enhance trust, while faster and personalized service is delivered through multi-channel strategies.
Personalization – A Key Trend in Digital Transformation
Businesses are embracing digital transformation to enhance the customer experience through personalization. By leveraging digital technologies, companies can deliver tailored experiences that boost customer satisfaction and engagement. Machine learning and big data analytics enable personalized content and recommendations. This allows businesses to meet customer expectations by providing relevant and timely information.
Digital transformation enables organizations to provide a seamless multi-channel experience, allowing customers to interact with the brand across different platforms effortlessly. By integrating these personalized experiences into their digital transformation journey, businesses can prioritize the needs of their customers and drive better customer experience.
How Personalization Elevates the Customer Experience?
Personalization plays a crucial role in enhancing the customer experience. Brands that thrive in customer experience (CX) surpass their competitors. According to a McKinsey study heightened customer satisfaction can boost revenue by up to 15% while reducing customer service costs by as much as 20%.
Businesses can offer customized products and services by tailoring the journey based on their preferences and needs. This improves customer satisfaction and creates a unique and memorable digital experience. With real-time personalized interactions, companies can provide timely and relevant information to their customers.
The Role of Automation in Enhancing Customer Experience
Automation enhances customer experience by streamlining business processes, reducing manual effort, and improving efficiency. With automation, companies can provide faster response times and better customer service, increasing satisfaction. Chatbots and AI-powered technologies automate customer support, ensuring round-the-clock assistance and enhancing the overall experience.
Automation enables businesses to deliver consistent experiences across different touchpoints, ensuring a seamless and cohesive customer journey. By automating repetitive tasks, companies can free up time to focus on providing a more personalized experience, catering to each customer’s unique needs.
Examples of Successful Automation Strategies
Successful automation strategies are revolutionizing the way businesses interact with their customers. Companies are leveraging automation to send personalized emails and targeted offers, enhancing the digital experience for customers. By providing self-service options, automation empowers customers to find answers independently, improving their overall user experience. It streamlines the collection and analysis of customer feedback, enabling organizations to improve their customer experience process continuously.
Real-time notifications and updates enhance customer satisfaction by keeping them informed and engaged. AI-powered chatbots have emerged as a game-changer, automating customer support and providing instant assistance, giving customers a better customer experience.
Ensuring an Agile IT Environment for Digital Transformation
Ensuring an agile IT environment is crucial for successful digital transformation. An agile IT infrastructure allows businesses to quickly adapt to changing customer demands, enabling them to stay ahead of the competition. Modern technologies like cloud computing provide flexibility and scalability, empowering organizations to integrate new digital technologies into their operations seamlessly. This agility is essential in supporting the implementation of new projects and initiatives that drive better customer experiences.
By maintaining an agile IT environment, companies can keep up with the fast pace of digital transformation, achieving their organization’s goals and delivering exceptional digital experiences to their customers. An agile IT environment sets the foundation for happy customers and a competitive edge in the digital landscape.
Are Companies Really Benefiting from Digital Transformation?
Companies are reaping the benefits of digital transformation. It gives a competitive edge, improves operations, reduces costs, and meets changing customer demands. Ultimately, successful digital transformation enhances the overall customer experience.
If you want to ensure that your business stays ahead in this digital era, you need to upskill your employees digitally. At TeKnowledge, our digital transformation experts are always ready to assess and create training solutions based on your business needs. Speak with us today.
- Blog & Industry Trends
In driving growth, many businesses prioritize core commercial activities in their digital transformation efforts—these are the functions and talent that directly contribute to achieving commercial goals. However, focusing solely on these areas overlooks the importance of non-core activities that shape the customer experience. While roles like customer service may be resource-intensive, they are just as crucial to your organization’s success as the products or services you offer. Often, businesses find it beneficial to outsource these specialized skills to enhance overall performance.
Why outsource non-core activity?
According to a survey by a software solutions provider, 83% of CIOs are under pressure to stretch their budgets and deliver digital transformation that will drive a positive impact on the business’s bottom line. And these same decision-makers are surrounded by economic headwinds like wage inflation in the talent markets and rising borrowing costs. So, what defines a cost-effective digital transformation strategy?
Clever resource allocation, and an understanding of where outside input may be more efficient. To alleviate the pressures they face, businesses should seriously consider outsourcing roles like tech support with a proven business partner.
Outsourcing offers access to top of the range dedicated industry expertise with proven, reliable service delivery. Rather than the time investment of identifying what digital transformation looks like for your non-core functions, an outsourcing partner will have already identified how to efficiently embrace new technologies like AI powered chatbots and virtual assistants.
Perhaps surprisingly, bringing in external expertise can often be the most economical option for a business, offering the quickest time to value. For instance, at TeKnowledge, our tech managed services reduce the need for extensive management oversight, allowing your internal talent to focus on driving business growth.
How can I ensure my outsourcing is successful?
In a gig economy, the piecemeal approach of hiring skills on an ad hoc basis may seem appealing, but it often leads to siloed benefits. Without a unifying strategic goal, these outsourced skill sets may not align with the broader business objectives, potentially creating long-term issues and even risking business failure.
Businesses should instead look for a long-term outsourcing partner, and one offering the right cultural fit. But it is important to vet partners carefully. For example, do they have the technical know-how to align with your operations? Are there clear communication channels and strong governance structures to ensure your organizations blend efficiently and hit the ground running?
Perhaps most importantly, you should ask yourself: do they understand my business priorities? For example, can the potential outsourcing partner help with security and mitigating regulatory risks? Is its own risk management framework up to standard?
Outsourcing optimizes your investment
Optimizing your investments in digital transformation by drawing upon experienced outsourced teams not only provides you with a collaborative partner that will truly embrace your business goals but frees up resources and management time to focus elsewhere, where the business needs it most for growth.
Structuring your approach to digital transformation in this way, around the dual prospects of functions driving business growth and functions providing supporting activity, can help ensure the long-term success of your investments in innovation. Using this framework of core vs. non-core strategy, the road ahead becomes an efficient and sustainable pathway to the next, digitally driven generation of your business.
Want to learn more about the benefits of outsourcing? Let’s chat.
- Events & Webinars , News & Company Updates
We are thrilled to announce that TeKnowledge Nigeria has been honored with the prestigious award for Africa’s Most Innovative Tech Support Services Company of the Year 2024 by the Africa Brand Awards. This accolade recognizes our relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation in providing top-notch tech support services across the continent.
The award ceremony, held at the Civic Center in Lagos, was a momentous occasion for TeKnowledge Nigeria. In attendance were key team members, including Olugbolahan Olusanya, Country Director for TeKnowledge Nigeria, Motunrayo Ayo-Akwe, Senior Marketing Manager for Africa, and Eric Uwaoma, Head of Sales for TeKnowledge Nigeria.
Motunrayo Ayo-Akwe expressed her excitement, stating, “This award is a testament to the quality of work we do. We are committed to continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible in providing digital transformation support to our customers, and this recognition inspires us to achieve even greater heights.”
Olugbolahan Olusanya echoed these sentiments, adding, “Winning this award is a significant milestone for TeKnowledge Nigeria. Considering that we have recently consolidated our business lines and the TeKnowledge name is still young, it is rewarding to receive this recognition. It validates our efforts and strategy in delivering cutting-edge tech solutions across Africa. I am extremely proud of the team and grateful to our clients and partners for their trust and support.”
- Events & Webinars
In today’s interconnected world, cybersecurity is essential for protecting data, maintaining continuity, and safeguarding trust. Yet, the industry faces a significant challenge: a lack of diversity. Underrepresentation of women and individuals from varied cultural and professional backgrounds limits creativity and innovation, posing serious security risks.
Embracing diversity is crucial to counteract increasingly complex cyber threats. This was a key theme at Duke University’s 3rd Cybersecurity Leadership Program (CLP2024), a prestigious event drawing over 100 registered participants from 16 countries, including regulators and CISOs from the USA, Latin America, Africa, Europe, Middle East and Asia.
The program provided a platform for C-level professionals to network, share best practices, and explore global cybersecurity developments. Key topics included legislation, strategy, the rise of AI and its implications in Cybersecurity, and emerging cyber threats, all emphasizing the crucial role of diverse teams in enhancing resilience and fostering innovation.
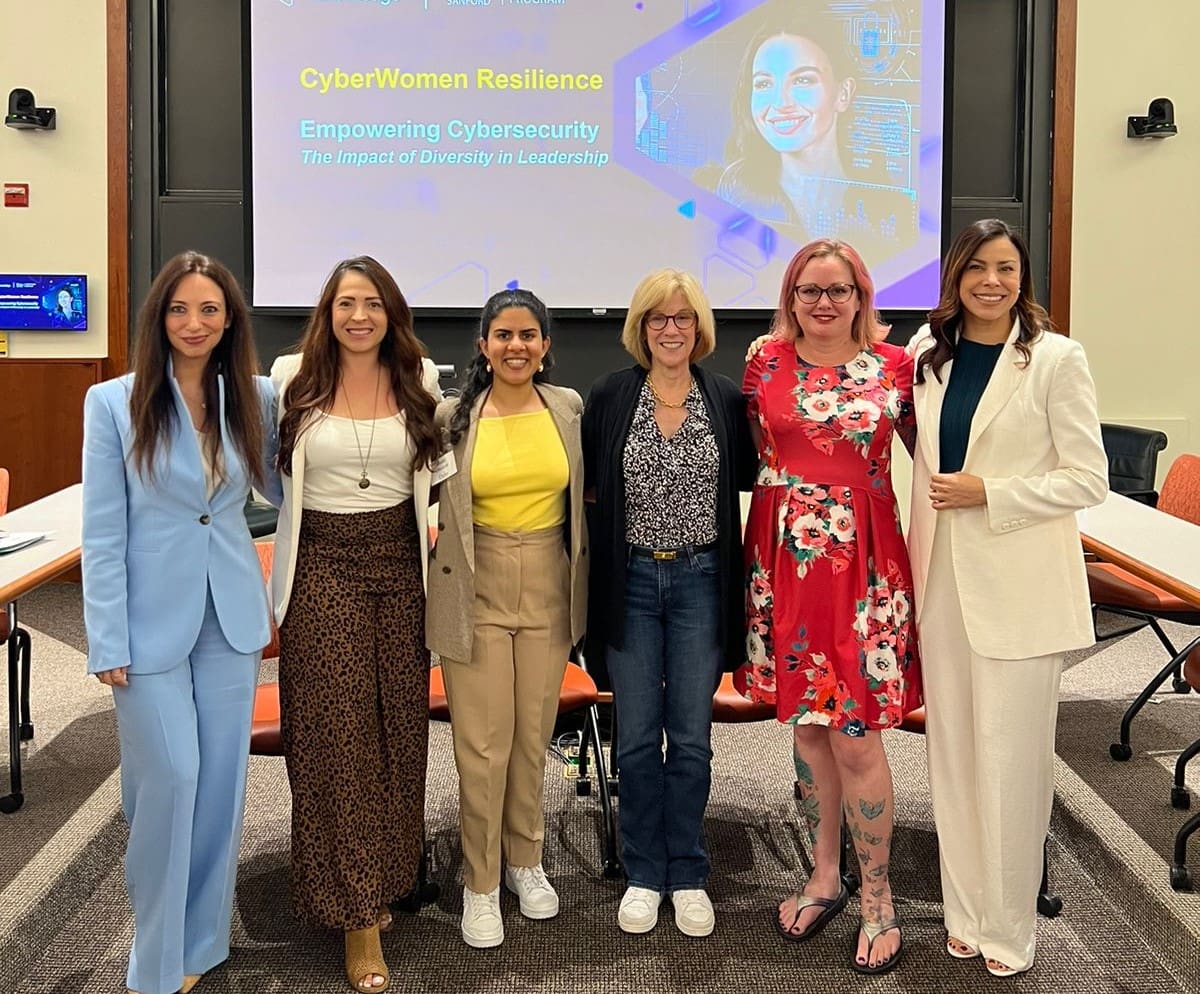
TeKnowledge was honored to support and join this conversation with leading thought leaders from major governments and enterprises. At the opening of CLP2024, our Executive Vice President María Balbás and Regional Leader for Latin America Jeannie Bonilla led the workshop “CyberWomen Resilience: Empowering Cybersecurity: The Impact of Diverse Leadership”. In this interactive session they engaged the executive audience with dynamic discussions on the value of diversity in cybersecurity, revealing how organizations and leaders can foster greater diversity with a modern and invigorating vision.
Ebani Dhawan, a Research Assistant at Duke University, began the session by presenting key statistics. She emphasized that empowering women is crucial for addressing the global talent shortage and managing the increasing complexity of cyber threats. Later, Camila Herrera, Graduate Research Assistant at Duke University; Jane Horvath, Partner at Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher LLP and former Chief Privacy Officer at Apple; and Bri Law, Deputy Coordinator at the Center for Cybersecurity Policy and Law, joined María and Jeannie for a panel discussion on the pivotal role of women in cybersecurity to inspire other women to join the industry.
Gender diversity in tech leadership roles introduces unique skills and perspectives, fostering inclusivity and innovation. Research from McKinsey shows that promoting gender diversity attracts top talent and mitigates biases.
Building on the success of previous editions in Abu Dhabi, Costa Rica, and the USA, TeKnowledge, in collaboration with Duke University, will continue to expand this program’s reach in the Middle East and Latin America. This commitment to fostering diversity and inclusion underscores TeKnowledge’s dedication to creating a collaborative, caring, and growth-oriented environment.
- Blog & Industry Trends
Understanding Managed Security Operations Centers
Managed Security Operations Centers (SOC) have become essential for businesses aiming to enhance their cybersecurity capabilities while alleviating the economic burden on their internal SOC. However, several misconceptions about Managed SOCs persist. This article will debunk these misconceptions and highlight the true value and benefits of Managed Security Operations Centers.
What is a SOC?
A SOC is a centralized hub responsible for proactively monitoring and managing an organization’s security posture. It serves as the organization’s defense nerve center, actively identifying and responding to potential cybersecurity incidents, vulnerabilities, and threats. SOCs employ advanced technologies, threat intelligence, and skilled security teams to provide enhanced protection against cyber threats. Their primary objective is to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems by identifying and mitigating potential cybersecurity incidents.
What is a Managed SOC?
A Managed SOC extends the capabilities of a traditional SOC by offering managed services. This outsourced security service provider manages an organization’s security operations, including threat detection, incident response, user behavior analytics, and more. With a Managed SOC, businesses gain access to a team of cybersecurity experts who continuously monitor their systems, identify threats, and respond swiftly to mitigate potential risks.
Key Services of a Managed SOC
The key services provided by a Managed SOC are crucial in maintaining a robust security posture for organizations. These services include:
- Monitoring and Threat Detection: Utilizing advanced detection capabilities such as security information and event management (SIEM) to identify and analyze potential threats.
- Incident Response: Swiftly responding to contain and neutralize threats, minimizing the impact on the organization.
- Threat Hunting: Actively searching for signs of potential threats, ensuring proactive protection against unknown threats.
- SecOps: Implementing, operating, and maintaining cybersecurity tools and solutions across the organization.
Four Common Misconceptions about Managed SOCs
Misconception 1: Managed SOCs are Only for Large Businesses
Many believe that Managed SOCs are exclusively for large businesses with extensive resources. This is far from the truth. Managed SOCs cater to organizations of all sizes, including small businesses, offering tailored cybersecurity solutions that align with specific needs and budgets.
Truth: Managed SOCs Provide Advanced Cybersecurity Solutions Accessible to Businesses of All Sizes
They partner with organizations as a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), leveraging their expertise to ensure scalable security operations. Whether it’s a small business or a large enterprise, Managed SOCs deliver solutions that prioritize security, visibility, and response capability.
Misconception 2: Managed SOCs are Expensive
There is a common misconception that Managed SOCs are prohibitively expensive. While establishing a SOC involves an initial investment, opting for a Managed SOC eliminates the need for direct investment, as costs are distributed among multiple entities.
Truth: Managed SOCs Deliver Security Services that are Both Effective and Cost-efficient in the Long Term
By collaborating with an MSSP, businesses can access advanced security operations, threat detection, incident response, and rapid response capabilities without incurring the high costs associated with staffing and maintaining an in-house SOC. The return on investment (ROI) is evident in the enhanced protection, proactive threat management, and improved cybersecurity posture businesses achieve.
Misconception 3: Complexity of Managed SOCs is Overwhelming
Another misconception is that Managed SOCs are overly complex. The perceived overwhelming nature of cybersecurity management often stems from a lack of awareness about the collaborative nature of Managed SOCs. A Managed SOC solution is less complicated because SOC experts are actively engaged in the process, working hand-in-hand with internal teams to provide valuable assistance and contribute to a clearer cybersecurity posture.
Truth: Managed SOCs Prioritize Simplicity and User-friendliness to Ensure Organizations can Easily Navigate and Utilize their Security Capabilities Effectively
By leveraging user-friendly interfaces and intuitive tools, Managed SOCs empower businesses to detect, respond, and hunt threats with ease, enhancing the overall security posture of organizations.
Misconception 4: All Managed SOC Alerts Require the Same Degree of Investigation
A common misconception is that all alerts generated by a Managed SOC require the same level of investigation. This belief fails to acknowledge the importance of prioritization in managing cybersecurity incidents. Managed SOCs employ advanced detection capabilities, threat intelligence, and incident response expertise to accurately prioritize alerts based on their potential impact and severity.
Truth: Proper Prioritization of Alerts is a Key Aspect of Managed SOC Services
By categorizing and prioritizing alerts, Managed SOCs enable organizations to allocate their resources effectively, focusing on incidents that pose the greatest risk. Through proactive threat hunting, incident response, and continuous monitoring, Managed SOCs contribute to cyber resiliency by ensuring organizations are equipped to handle emerging threats, unknown vulnerabilities, and persistent cybercriminals. Prioritization allows businesses to respond swiftly to critical incidents, reducing downtime, mitigating potential damage, and maintaining a strong security posture.
Conclusion
Debunking common misconceptions surrounding Managed SOCs is crucial for businesses to fully harness the benefits of a proactive security approach. Managed SOCs are not exclusive to large organizations; they cater to businesses of all sizes, providing cost-effective solutions. The complexity of Managed SOCs is overstated, as they offer simplicity and user-friendliness. Additionally, not all Managed SOC alerts require the same degree of investigation; they prioritize and address high-risk threats promptly. Embracing Managed SOCs is essential for enhancing cyber resilience and safeguarding your business from evolving threats. Stay ahead of the curve by leveraging the expertise and resources of a Managed SOC with TeKnowledge. Reach out to explore our comprehensive range of services designed to help you navigate the complexities of digital transformation and cybersecurity with confidence.
- Blog & Industry Trends
Exploring the Strategic Advantages of Offshore Outsourcing with TeKnowledge
When considering outsourcing, many organizations gravitate towards offshore models, attracted by the potential for lower labor costs and access to burgeoning markets. At TeKnowledge, we understand that the decision to outsource is pivotal, and with various outsourcing models available, it’s crucial to choose one that aligns with your strategic goals. If offshore outsourcing is the path you are considering, rest assured, this guide is designed to arm you with essential knowledge to select the most suitable outsourcing partner for your needs.
What is Offshore Outsourcing?
Offshore outsourcing occurs when an organization engages an external supplier to perform services or manufacture products in a country different from where the company is headquartered. This strategy is leveraged to capitalize on economic efficiencies, such as lower labor costs and specialized skills unavailable domestically, enhancing operational agility and enabling round-the-clock business processes.
The Benefits of Offshore Outsourcing
Access to Elite Talent: Offshore outsourcing opens the doors to a global talent pool, offering specialized skills that are often rare or cost-prohibitive in your home country. This access allows organizations to augment their capabilities and explore new business ventures with agility and expertise.
- Cost Efficiency: One of the most compelling reasons for offshore outsourcing is the significant reduction in labor and operational costs. Engaging with markets where the economic conditions differ from those at home can lead to substantial cost savings. However, it is vital to approach this advantage with an ethical mindset, considering the socio-economic impact on the supplier region to maintain and enhance your organization’s global reputation.
- Continuous Productivity: The geographical spread across time zones enables non-stop operations, ensuring that your business remains operational after your local offices have closed. This is particularly beneficial for functions that require 24/7 support, such as customer service desks.
- Insights into Diverse Markets: Collaborating with an offshore partner not only facilitates entry into new markets but also provides deep insights into local consumer behavior and market dynamics. This strategic advantage can significantly reduce the risks and costs associated with geographical expansion, allowing for scalable and flexible business operations.
Navigating the Challenges of Offshore Outsourcing with TeKnowledge
While offshore outsourcing offers numerous strategic advantages, it is imperative to understand and manage its potential drawbacks effectively. TeKnowledge is committed to providing insights that help organizations navigate these challenges with foresight and precision.
Potential Drawbacks of Offshore Outsourcing
- Security Risks: Sharing sensitive data with external partners is essential in offshore outsourcing, but it often raises data security concerns. At TeKnowledge, we provide a significant advantage with our cybersecurity expertise. Our clients gain peace of mind knowing that their data, as well as their customers’ data, is safeguarded by a team of cybersecurity experts trusted by governments and enterprises globally. We ensure your data is protected through robust security protocols and strict compliance with international standards.
- Reduced Control: Offshore outsourcing may result in decreased control over certain business processes and outputs. This can affect project flexibility and response times to changes. TeKnowledge advises establishing clear communication channels and contractual agreements that include flexible terms to manage changes effectively, ensuring alignment with your strategic goals.
- Operational Standards and Timelines: The external providers’ different operational methods and adherence to their own timelines can pose challenges. We recommend selecting partners who demonstrate alignment with your business practices and can integrate seamlessly with your operations to mitigate these risks.
- Time Zone Differences: The variance in time zones can impact the working dynamics between your team and the outsourced provider. While this can extend productive hours, it may also complicate real-time communication. TeKnowledge suggests strategies such as overlapping work hours and utilizing asynchronous communication tools to enhance efficiency and ensure continuous collaboration.
Offshore vs. Onshore Outsourcing
- Location and Cost Considerations: The primary distinction between offshore and onshore outsourcing lies in the location of the outsourcing partner. Offshore outsourcing is typically more cost-effective and provides access to a broader skill set globally. In contrast, onshore outsourcing, while often more costly due to higher local wages, offers benefits in terms of communication ease, cultural alignment, and collaborative efforts.
- Strategic Decision Making: Choosing between offshore and onshore outsourcing depends on various factors including budget constraints, communication requirements, and the nature of the work. Offshore outsourcing is advantageous for leveraging cost efficiencies and accessing global talent, whereas onshore outsourcing is preferable for projects that require close interaction and shared cultural and regulatory frameworks.
Exploring the Spectrum of Offshore Outsourcing Models with TeKnowledge
Offshore outsourcing offers a versatile array of services that cater to diverse business needs across industries. At TeKnowledge, we understand the strategic importance of selecting the right outsourcing type to enhance your operational capabilities and drive innovation.
Types of Offshore Outsourcing
- Production Offshoring (Business Process Outsourcing – BPO):
Business Process Outsourcing involves delegating non-core functions to external parties, optimizing both front-office and back-office operations. Front-office services include direct customer interactions like customer support, telemarketing, and technical assistance. Back-office services, on the other hand, focus on internal needs such as HR, accounting, and specialized tasks like web and mobile development, ensuring your core team can focus on strategic objectives.
- System Services Offshoring (Information Technology Outsourcing – ITO):
This form of outsourcing is centered around IT-centric services including software development, network management, and cloud computing. Leveraging global IT expertise, TeKnowledge helps organizations enhance their technological infrastructure and capabilities, ensuring they remain at the cutting edge of industry standards and innovations.
- Reshoring (Onshoring or Backshoring):
Reshoring refers to the strategic shift of bringing outsourced services back to the company’s home country. This trend is often driven by the need for greater control over business processes, quicker market responsiveness, and adherence to ethical and environmental standards. TeKnowledge supports organizations in navigating the complexities of reshoring, aligning with their strategic imperatives for enhanced governance and localized engagement.
Business Activities Suitable for Offshore Outsourcing
- IT Services:
IT outsourcing encompasses a broad range of services, including but not limited to technical support and network management, cybersecurity, and cloud services. Offshore IT services enable around-the-clock monitoring and management of systems, benefiting from global time zone variations to maximize productivity and security.
- Customer Success:
Offshoring customer success functions allows businesses to provide continuous support through extended service hours, covering different time zones and languages. This model not only enhances customer satisfaction but also allows your core team to concentrate on high-value interactions and complex problem-solving.
- Software Development Services:
Software development is inherently suited for offshore outsourcing due to the universal nature of coding languages. Offshore development can accelerate delivery timelines and tap into global technological expertise, driving faster innovation and competitive advantage.
- Other Front Office Services:
Additional services such as digital marketing, content creation, and sales support can also be effectively outsourced. These services enable organizations to scale their outreach and customer engagement efforts without diluting focus from core business strategies.
Should Companies Outsource in 2024?
The straightforward answer is yes. The outsourcing industry has witnessed robust growth throughout 2023, with promising indicators for continued expansion into 2024 and beyond. According to a report from Statista, the managed services market experienced an 11.9% growth from 2022 to 2023 and is anticipated to grow by an additional 10.3% in 2024.
Furthermore, global spending on IT services has also seen a significant uptick, increasing by 8.8%, or $115.21 million in 2023. The Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) sector has been particularly noteworthy, with a report from Grand View Research highlighting that the global BPO market reached $261.9 billion in 2022 and is projected to escalate to $525.2 billion by 2030.
What Is the Best Country for Offshore Outsourcing?
The choice of location for offshore outsourcing can significantly impact your organization’s operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. While many regions offer outsourcing services, countries such as Vietnam, China, Bulgaria, Costa Rica, and Nigeria stand out for their unique advantages in the tech sector. It is essential to conduct thorough research to understand the specific benefits and challenges each location presents and how they align with your organizational needs.
How to Pick the Right Offshore Outsourcing Company
Choosing the right outsourcing partner is crucial for leveraging the full potential of offshore capabilities. Here are some key steps to guide your decision-making process:
- Identify Essential Services: Determine the specific services your organization needs to outsource to enhance focus on core competencies.
- Define Outsourcing Needs: Understand the type of outsourcing—whether technical, customer support, or development—that will best support your strategic goals.
- Weigh Pros and Cons: Carefully assess the advantages and potential challenges of offshore outsourcing, considering factors like cultural compatibility, time zone differences, and communication barriers.
- Evaluate Locations: Analyze different outsourcing locations, focusing on factors such as talent availability, cost efficiency, political stability, and technological infrastructure.
TeKnowledge Offshore Outsourcing Services
At TeKnowledge, we understand the transformative impact of offshore outsourcing. With our deep industry expertise, commitment to operational excellence, and a global network of resources, we are equipped to enhance your business operations through strategic outsourcing solutions. Our services are designed not only to offer cost savings and continuous support but also to infuse your projects with advanced technical expertise, ensuring that your path to success is both innovative and efficient.
By partnering with us, you can confidently navigate the complexities of global outsourcing and harness its benefits to achieve sustained growth and competitive advantage. Reach out today to learn more.
- Events & Webinars
TeKnowledge continues to lead the charge in digital transformation, empowering governments and enterprises globally. Our unwavering commitment to technology enablement uniquely positions us to help our clients navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence and a competitive edge. The first week of July 2024 was a testament to our mission in Nigeria, as we made significant strides at three major events: IOT West Africa, the LSETF Future of Employment Summit, and the MarkHack Conference. Each of these gatherings showcased our expertise, ignited engaging discussions, and strengthened our network, reinforcing TeKnowledge’s role as a transformative catalyst in the tech industry.
Securing the Future of IoT: Olugbolahan Olusanya at IoT West Africa
TeKnowledge kicked off the month with a powerful presence at IOT West Africa, which took place at The Balmoral Convention Centre, Federal Palace Hotel, from 2nd to 4th of July, 2024. Our Nigeria Country Director, Olugbolahan Olusanya, captivated the audience with his compelling presentation on “Cybersecurity Challenges in the IoT Ecosystem.” Olugbolahan’s deep dive into the labyrinth of IoT cybersecurity threats was not just informative but a wake-up call for many. His passionate delivery emphasized the urgent need for robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect the interconnected world we live in. The session sparked lively discussions and left the audience with a renewed sense of vigilance and proactive strategies to counter cybersecurity threats.
Equipping the Workforce for the Future: LSETF Future of Employment Summit
The future of work is rapidly evolving, and TeKnowledge recognizes the importance of a skilled and adaptable workforce. Our commitment to this was underscored by our participation in the LSETF Future of Employment Summit, a crucial platform exploring the future workforce landscape under the theme “Job Creation: Uniting for Impact – Create, Collaborate, Change.”
In this event, our team immersed themselves in the vibrant discussions about how technology is reshaping job markets and the essential skills needed for future employment, reiterating our dedication to not just follow but influence the trajectory of employment trends and skills development. At our exhibition booth, we engaged multiple partners and prospective customers on how our Digital Skilling, Technical Managed Services and Cybersecurity offerings could help their businesses. A major highlight of the summit was the launch of the Lagos State Labour Market Information System (LMIS), a one-stop platform designed to provide relevant labour market-related data that informs actionable decisions in Lagos.
The networking opportunities were abundant, and we left with new alliances and insights that will drive our initiatives forward.
Revolutionizing Customer Experience with Emerging Technologies: Olugbolahan Olusanya at MarkHack Conference
Customer experience is paramount in today’s competitive landscape. At the MarkHack Conference on July 5th, the Nigeria Country Director, Olugbolahan Olusanya delivered a captivating keynote speech titled “Harnessing Emerging Technologies To Revolutionize Customer Experience.”
His presentation delved into how businesses can leverage emerging technologies to create personalized, engaging, and secure customer experiences, and demonstrated how TeKnowledge has efficiently used said technologies to support our partners and enhance customer experiences. Additionally, TeKnowledge’s Senior Marketing Manager (Africa), Motunrayo Ayo-Akwe, played a vital role as a hackathon mentor, guiding and inspiring Suba Capital, one of the startup companies that pitched for the hackathon.
TeKnowledge: Unleashing Tech Potential, Step by Step
TeKnowledge stands as the transformative catalyst for digital evolution, providing governments and enterprises worldwide with unparalleled cybersecurity services, advanced technical skilling, and enterprise technical services at scale. Our commitment to technology enablement, security, and advancement positions us uniquely in the market, ensuring our customers are equipped to achieve their strategic imperatives in the digital age with confidence and competitive advantage.
Stay tuned for more exciting updates as TeKnowledge continues to be a driving force in shaping a secure and innovative future!